“Jim and Mike brought the company to where it is … which is part of the biggest problem they’re facing,” said Charter Equity analyst Ed Snyder, who has covered RIM since its public listing in 1997, two years before the BlackBerry was launched.
“They’re stuck in the past. They know what worked and keep playing that card and it’s not working any more, and they don’t seem to have any ideas,” he said.
via BAY STREET-As RIM struggles, talk of a change at top surfaces | Reuters.
In the case of Apple, the departure of the founder is considered a grave threat to the continuing success of the company.
In the case of RIM and Microsoft, the continued tenure of the founders is considered a grave threat to the success of the company.
Clearly, the theory that founders of successful companies can assure continuing success is flawed. Coupled to that implied causality is that departure of founders is always a problem.
Both are reflections of the idea that companies are predominantly successful (or fail) because of the skill (or incompetence) of a small group of individuals.
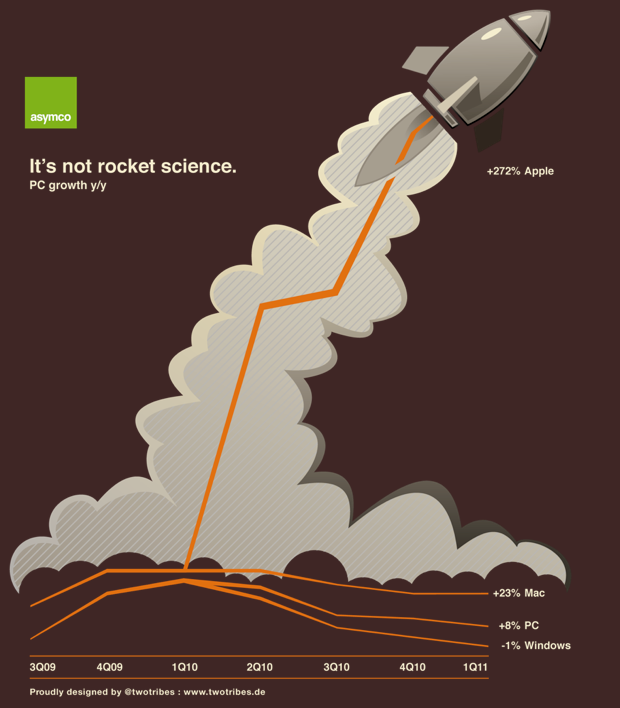
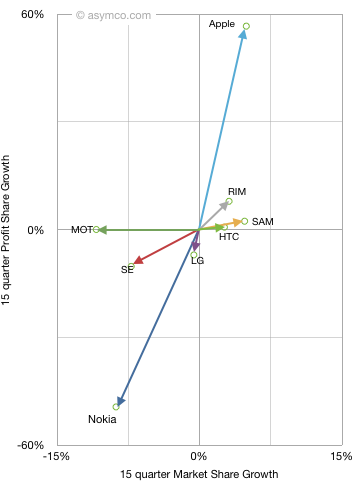
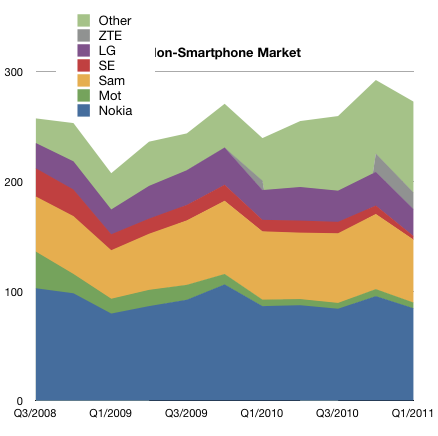
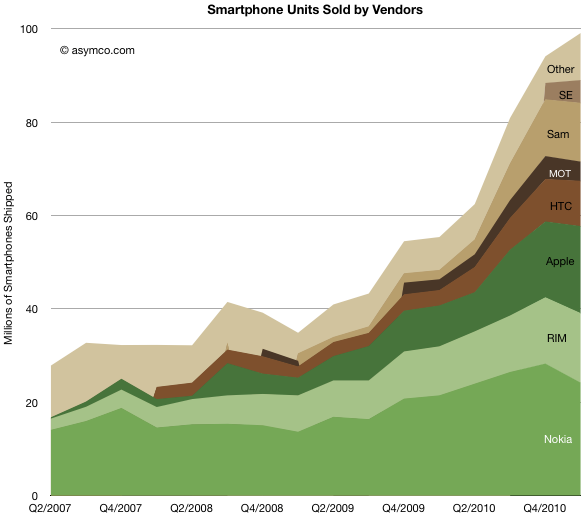
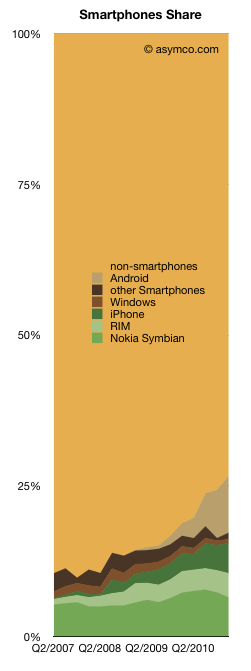
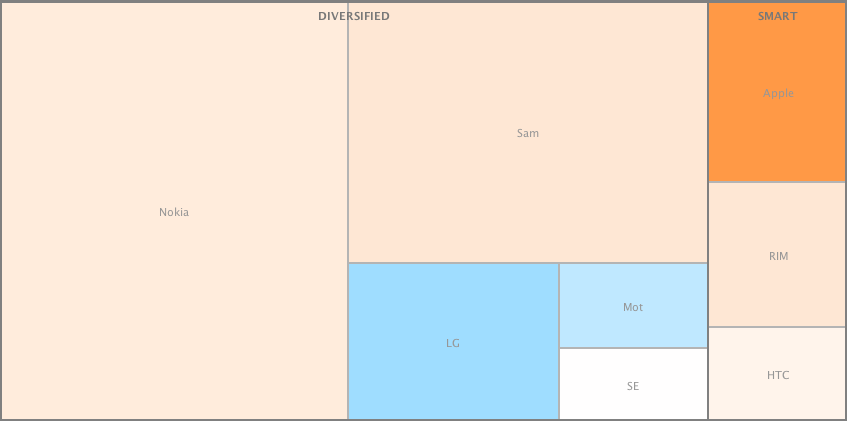
What the idea fails to explain is why companies fail (or succeed) as a cohort. RIM’s troubles are similar to Microsoft and to Nokia’s. Did they conspire or collude to fail simultaneously? Historically, incumbents fail simultaneously, regardless of who’s in charge.
And what about the problem that a company goes from success to failure (and vice-versa) while the same management is in charge. The “smart manager” theory of company success is as pervasive as the “stupid manager” theory of company failure. The perplexing thing is that while both of these theories are applied within the lifetime of a company, the management does not change.